What Is The Risk For Prostate Cancer After A Negative Biopsy
Confirm MDx works on the DNA level to help identify undetected cancers. The test is able to detect abnormal changes to DNA associated with the presence of prostate cancer. Since these changes are at the molecular level they can not be seen by the standard microscopic evaluation traditionally used for all prostate biopsies.

ConfirmMDx is a Well-Validated Epigenetic Test that Guides the Detection of Occult Prostate Cancer on a Patient’s Previously Biopsied Negative Tissue
• The use of ConfirmMDx for prostate cancer detection using methylation-specific PCR (MSP) and cancer-associated epigenetic biomarkers to improve upon histopathology has been well validated in both scientific and clinical studies.
• DNA methylation, the most common and useful measure of epigenetic abnormality testing, is responsible for the silencing of key tumor suppressor genes. DNA methylation biomarkers associated with prostate cancer have been extensively evaluated. More than 55 studies on the ConfirmMDx genes and technology have been published in peer-reviewed, scientific and medical journals.
• GSTP1 is the most intensely studied and widely reported epigenetic biomarker associated with prostate cancer diagnosis, encoding the glutathione S-transferase Pi 1 protein involved in detoxification, due to its high sensitivity and specificity.
• Complementing GSTP1, methylation of the APC and RASSF1 genes is frequently found in prostate cancer, and these markers have demonstrated a “field effect” aiding in the identification of biopsies with false-negative histopathological results.
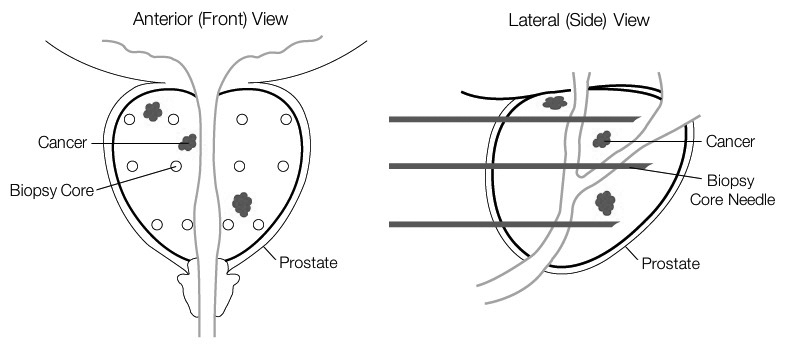
• The concept of a field cancerization effect, when first reported in medical literature by Slaughter in 1953, described the changes in tissues surrounding cancer lesions and their association with development of tumors. Later, the term “field effect” evolved to include molecular changes in adjacent, benign-looking tissues. The epigenetic field effect is a molecular mechanism whereby cells adjacent to cancer foci can contain DNA methylation changes, which may be indistinguishable by histopathology, but detectable by MSP testing. The presence of epigenetic field effects associated with prostate cancer has been widely published and is the basis of activity for the ConfirmMDx assay to aid in the detection of occult prostate cancer on previously biopsied, histopathologically negative tissue.
ConfirmMDx Addresses Prostate Biopsy Sampling Error and the False-Negative Biopsy Dilemma
“Rule-in” high-risk men who have had a previous negative biopsy result, may be harboring undetected cancer (a false-negative biopsy result), and therefore may benefit from a repeat biopsy and appropriate treatment.
“Rule-out” otherwise cancer-free men from undergoing unnecessary repeat biopsies and screening procedures, helping to reduce complications, patient anxiety, and excessive healthcare expenses associated with these procedures.
ConfirmMDx Key Benefits
Incorporating ConfirmMDx into clinical practice improves patient stratification so you can focus on finding aggressive prostate cancer.
-
Specific information for GS≥7 (GG≥2) prostate cancer
-
Clinically validated in African American men
-
Saves the healthcare system $588 per patient
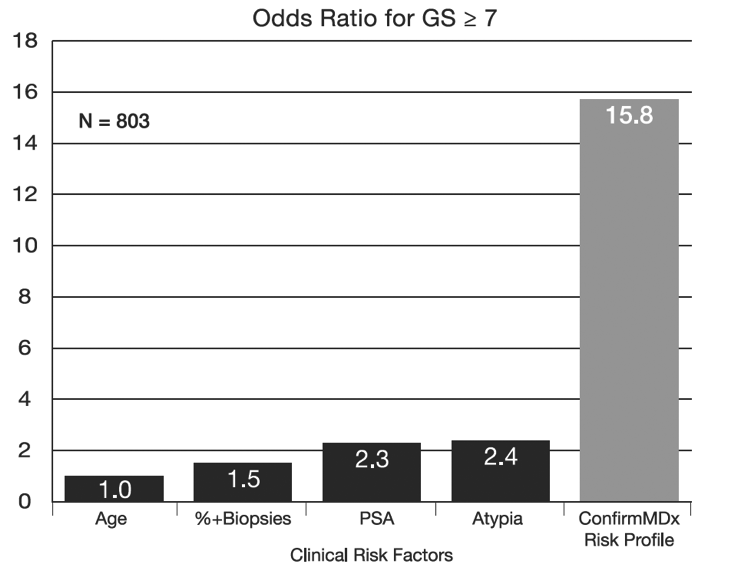
The Most Significant Predictor of Prostate Cancer Detection on Repeat Biopsy
Independently published clinical studies have shown that for men who have received a negative prostate biopsy result, ConfirmMDx is the single most significant predictor of patient outcome among all currently available clinical factors, such as age, PSA level, and DRE results.
Of an estimated 500,000 biopsies performed each year, less than one-third actually result in a cancer finding, leaving more than 300,000 men with a negative biopsy reading but still facing elevated clinical risk factors.3,11,12 Concerns over inconclusive (false-negative) biopsy results, coupled with the high rate of clinically significant cancer detected upon repeat biopsy, pose a diagnostic dilemma:
-
43% of patients with negative histopathology on initial biopsy will undergo a repeat biopsy, many also continuing on to 3rd and 4th biopsies.
-
Repeat biopsies are invasive procedures resulting in increased risk of infection and hospitalization.
-
Significant costs are associated with unnecessary procedures and associated risks.